Amazon EC2
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) : EC2 allows scalable deployment of applications by providing a Web service through which a user can boot an Amazon Machine Image to create a virtual machine, which Amazon calls an “instance”, containing any software desired. A user can create, launch, and terminate server instances as needed, paying by the hour for active servers, hence the term “elastic”.
Step 1. Launch an instance (Ubuntu linux)
- a. Sign in your aws account and then open EC2 dashboard.
- b. Launch an instance.
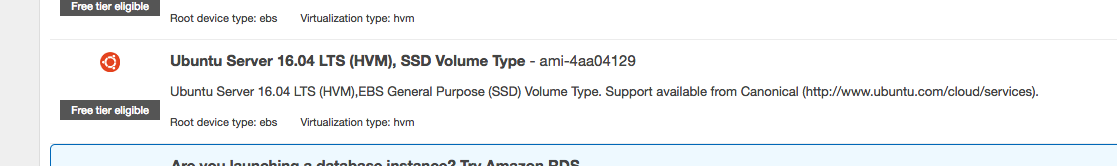
- c. Select the Ubuntu Server 16.04 image.
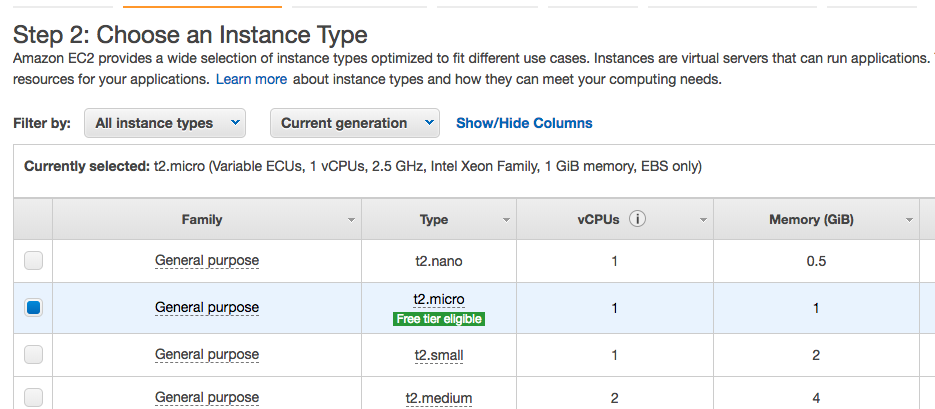
- d. Use t2.micro as instance (free). Click next instead of launch.
- e. Jump to security group setup. Add ports and set sources (determine the traffic that can reach the instance).
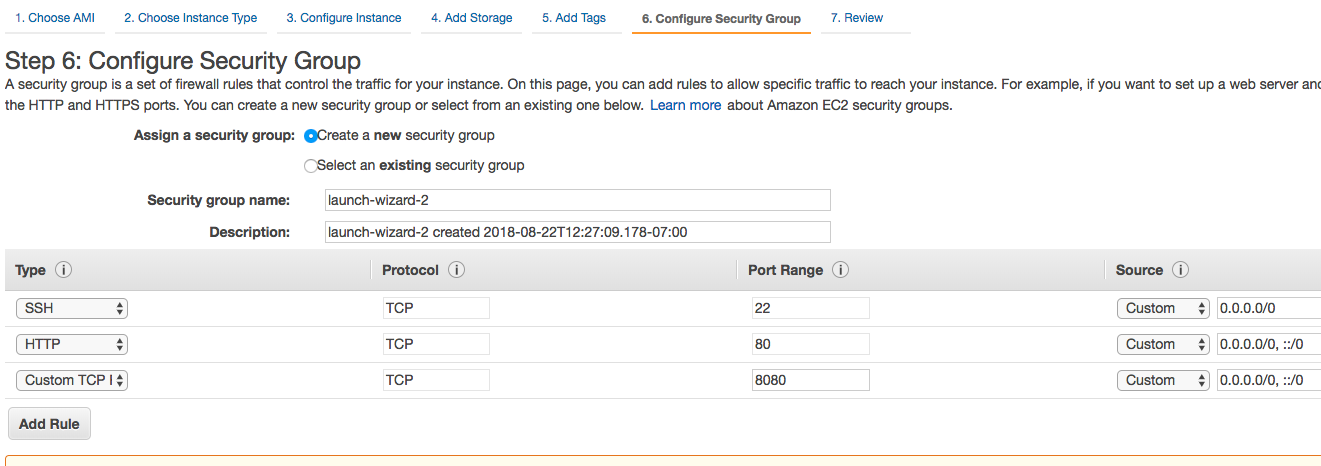
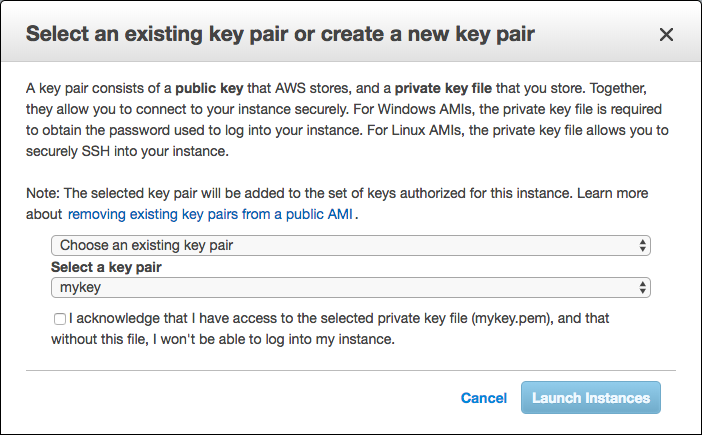
- f. Click Launch. You will be asked to create and name a new key pair and download the private key.
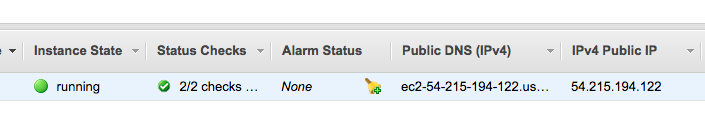
- g. Wait for the instance to initialize.
Step 2. Connect to the instance
Open your terminal, run:
1 | chmod 600 /path/to/mykey.pem |
if asked “Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? ”, type “yes”, enter.
You are now on the remote server, you can play with Linux commands:
->hostname, ifconfig, whoami, uptime, pwd, ls
Step 3. Install Java, MySQL and Tomcat 9
Install Java
In your instance’s terminal, execute the following commands:
1 | sudo apt-get update |
Verify the java version:
1 | java -version |
Install MySQL
1 | sudo apt-get install mysql-server |
Then execute your import database sql file in the mysql shell.
Install Tomcat
Execute the following commands:
1 | cd /opt/ |
Verify with http(s)://YOUR_INSTANCE_IP:PORT_NUMBER/
Step 4. Run Application on EC2
This part will use java-based web application as example.
WAR file
WAR file (or Web application ARchive) is a JAR file used to distribute a collection of JavaServer Pages, Java Servlets, Java classes, XML files, tag libraries, static web pages (HTML and related files) and other resources that together constitute a web application.
Export WAR file(in Eclipse)
- a. verify your website works correctly on local environment.
- b. open your database config file (e.g. MySQLDBUtil.java), change and make sure port is 3306, and username and password are correct(e.g. ‘root’).
- c. In Eclipse, select File->Export->Web->war File, save the war file to disk.
- d. Copy the war file to your instance:
1 | scp -i /path/to/mykey.pem /path/to/warfile ubuntu@YOUR_INSTANCE_IP:~/ |
- e. In your instance’s terminal(remote), type the following command:
1 | sudo cp ~/yourwarfile /opt/tomcat/webapps/ |
- f. Verify the server on the browser
Some Configurations
Change the HTTP port from 8080 to 80
- a. On the remote command-line terminal, edit the tomcat configuration by:
1 | sudo vim /opt/tomcat/conf/server.xml |
- b. Press i to enter insert mode, type :69 to go to line 69:
1 | <Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" |
Change 8080 to 80.
- c. Press ESC to exit insert mode, then type :wq to save and exit.
- d. Restart tomcat by:
1 | sudo /opt/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh |
- e. Visit your website to see if the server is started correctly.
Make tomcat auto start when Linux boots
- a. On the remote command-line terminal, type the following command:
1 | sudo vim /etc/init.d/tomcat |
- b. Press i to enter the INSERT mode, then paste the following contents:
1 |
|
- c. Save and Exit.
- d. Make the new file executable:
1 | sudo chmod +x /etc/init.d/tomcat |
- e. Update bashrc to catch your script:
1 | sudo update-rc.d tomcat defaults |
- f. You can also use following command to manually restart tomcat:
1 | sudo /etc/init.d/tomcat restart |
Make tomcat auto restart everyday
Your web app may be not that stable to run for months. You can restart it every night to keep it healthy.
- a. On your instance’s terminal, type the following command:
1 | sudo crontab -e |
- b. Input 3 to select vim.basic as the editor
- c. Move the cursor to the end, press i to enter edit mode. Input the following, It means restart tomcat at 1:00 and 13:00 UTC everyday:
1 | 0 1,13 * * * sudo /etc/init.d/tomcat restart |
- d. Save and exit.
Remote Debug
You can check Java error from Tomcat runtime log. Location:
1 | /opt/tomcat/logs/localhost.<date>.log |
e.g. /opt/tomcat/logs/localhost.2018-8-21.log
Check tomat process
1 | ps aux|grep tomcat |
To kill the process:
1 | sudo kill -9 17273 |
Others
Learn vim:
1 | vimtutor |
Learn emacs:
1 | C-h t |